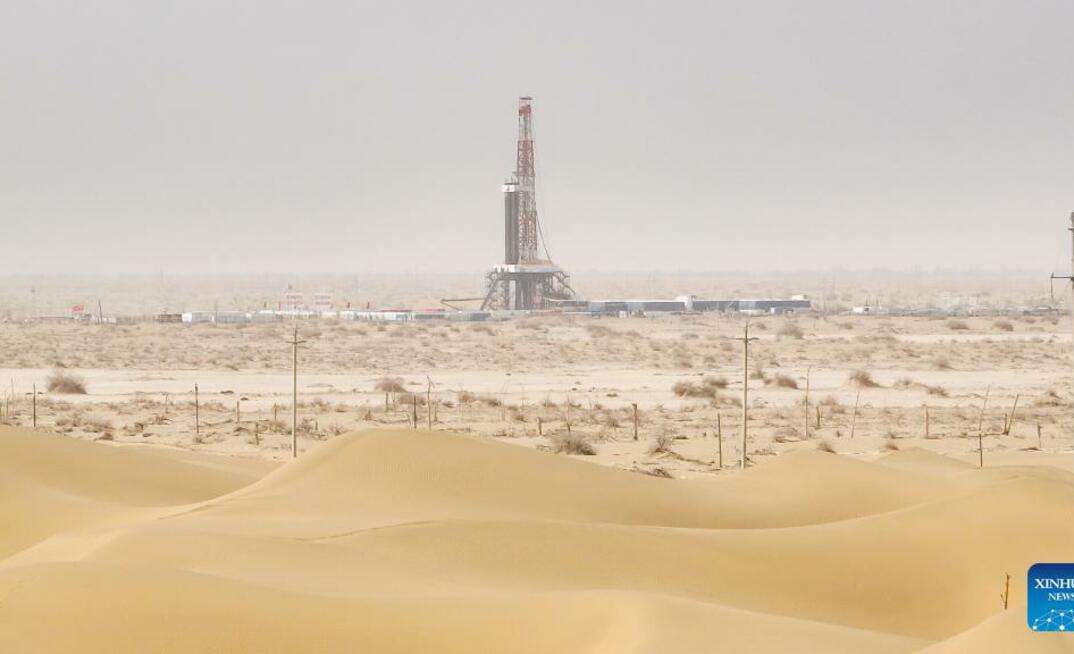
Located in the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert in the Tarim Basin, the Shenditake 1 is expected to reach a designed depth of 11,100m upon completion. It is China's first scientific exploration borehole designed to exceed a depth of 10,000m.
Since the start of drilling on May 30, 2023, the borehole has penetrated 13 continental strata, with more than 1000 drill pipes driven into the Earth and over 20 drill bits consumed in the process.
"It is the first time that China has drilled a vertical borehole over 10,000m deep," Wang Chunsheng, chief expert of the Tarim Oilfield of China National Petroleum Corporation, which is in charge of the drilling, said.
Wang said that after reaching 10,000m, the drilling will face more severe challenges such as temperatures of over 200 degrees Celsius and formation pressure exceeding 130MPa, and the difficulty will multiply with each meter drilled deeper.
The deepest vertical well in the world today has a depth of more than 12,262m. Jia Chengzao, an academician at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said the Shenditake 1 has become the second deepest vertical well worldwide and the deepest in Asia, and is of milestone significance in deep-Earth scientific research and ultra-deep oil and gas exploration.